General information
Fluoroplastics belong to the family of thermoplastics. Due to their high molecular weight, polytetrafluorethylene cannot be processed with the classic thermoplast methods like injection moulding or extrusion. Both materials are transferred from powder form to semi-finished products by using special press-sintering techniques or the so called paste extrusion. All other fluoropolymers like PFA, FEP, ETFE, ECTFE, PVDF, THV or PVF are processed using the known production methods for thermoplastics. The fully fluorinated materials PFA and FEP in particular require a corrosion resistant construction of the processing machines. With increasing the content of fluorine, the fluoropolymers offer a better chemical and higher thermal load.
Especially PTFE, PFA and FEP have the following unique properties:
- almost universal chemical resistance
- high thermal load capacity (–200 °C up to +250 °C)
- non-flammable
- resistant to environmental changes (weather, light)
- non-adhesive
- ultra low friction coefficient
- unbreakable
- physiologically safe
- inert, tasteless, odourless
- UV-resistant
- not ageing, the properties do not change even during long-term storage
- without any aggregates like plasticizers or antioxidants
- unlimited sterilization with steam or ethylene oxide possible. A sterilization using high-energy radiation is not recommended.
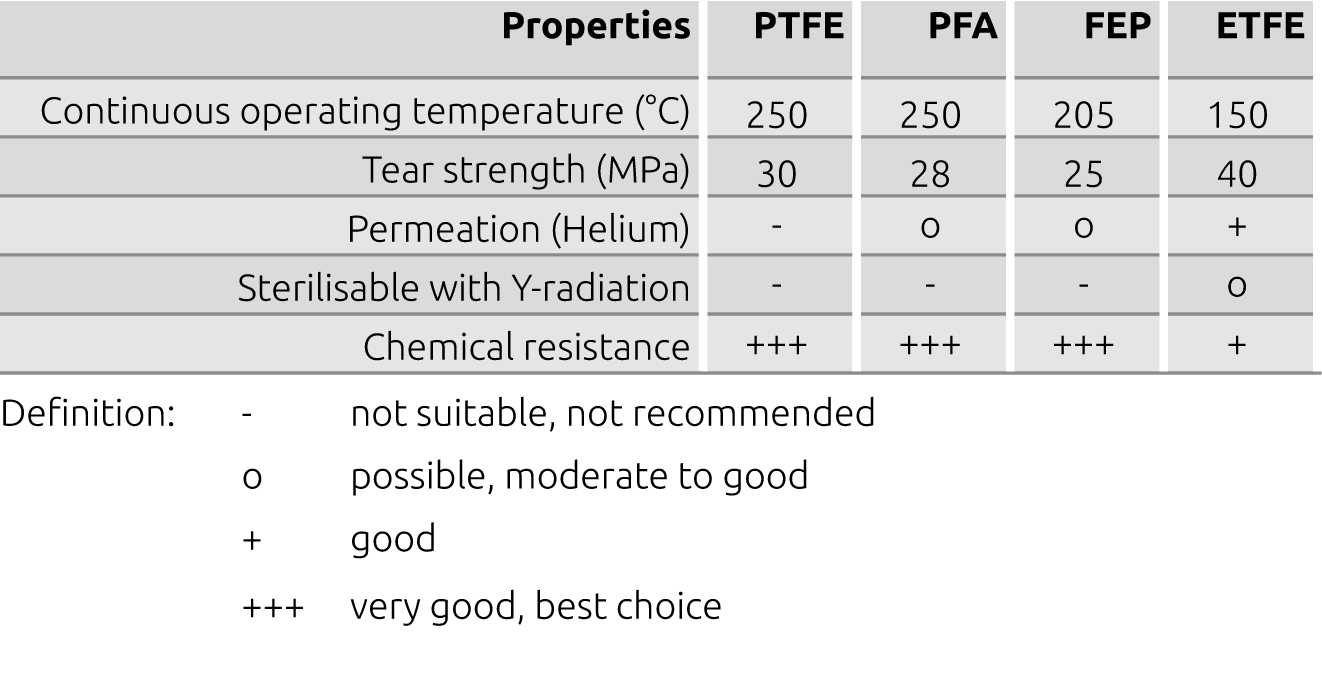
All other fluorinated thermoplastics include beside the fully fluorinated monomer block tetrafluorethylene additional, non-fluorinated components. This allows to adapt systematically the properties and thus to facilitate the processing and to enlarge the range of applications.The chart below gives some general advice on the choice of the best suitable fluoropolymers: