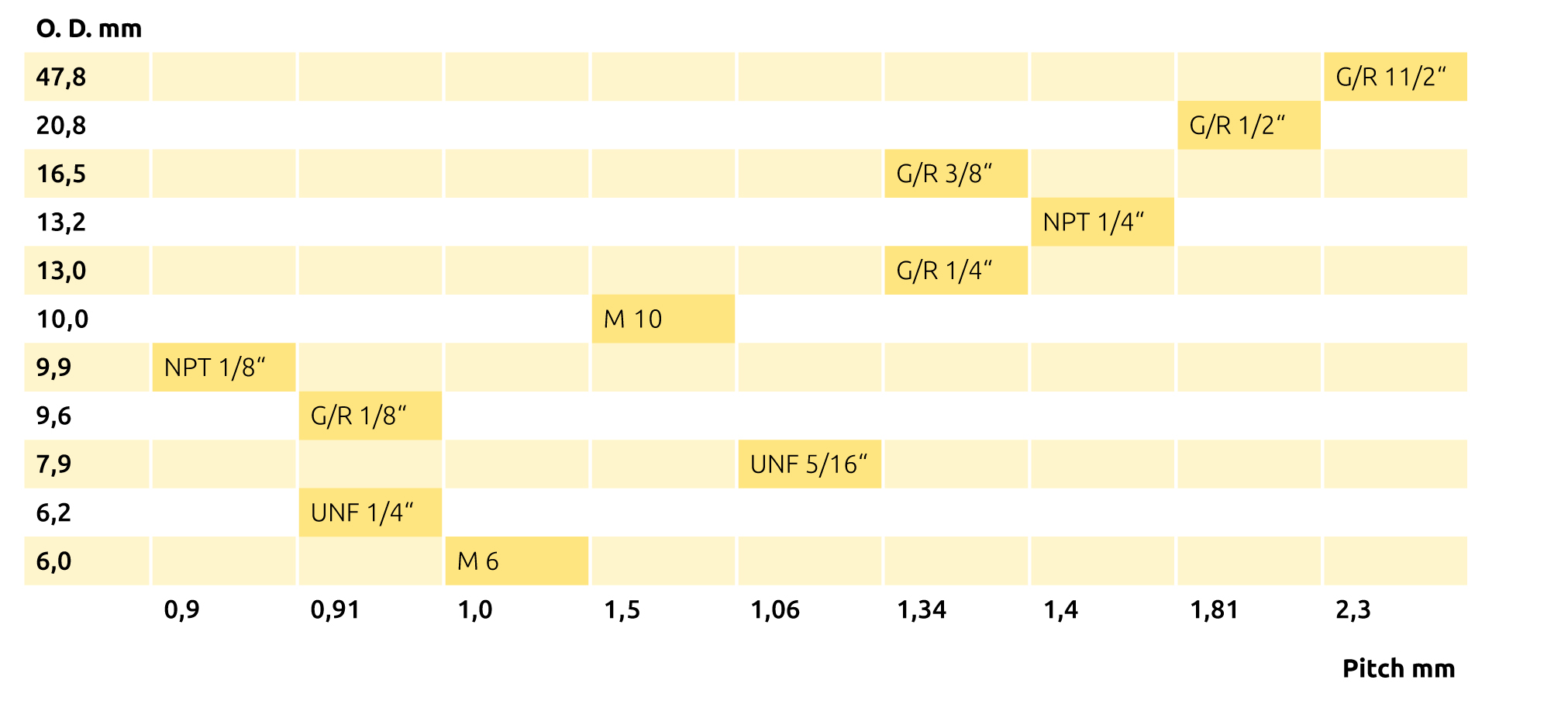
Connection threads
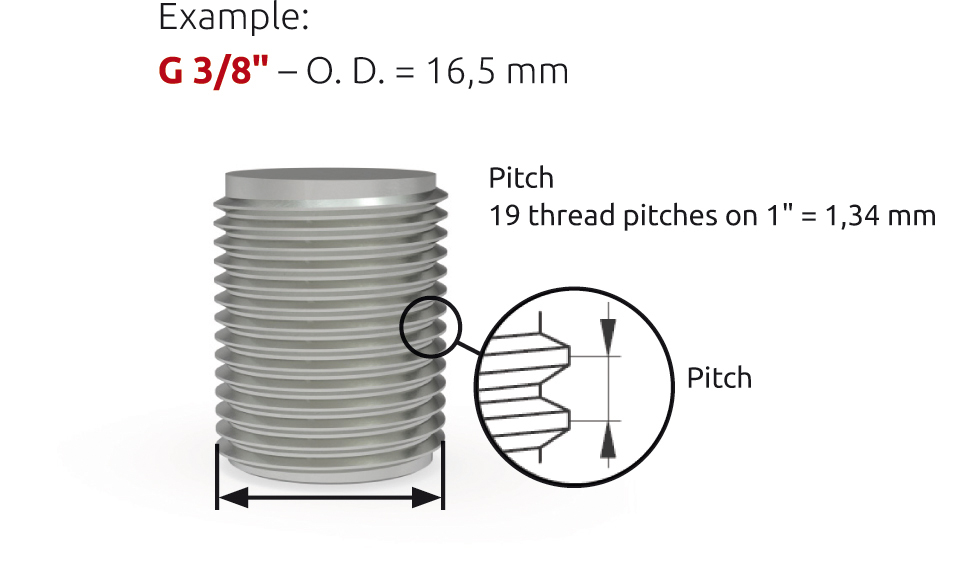
G or R and BSP
- Main use in countries with imperial system
- G-threads: cylindrical O. D. and I. D.
- R-threads: tapered O. D. and cylindrical I. D.
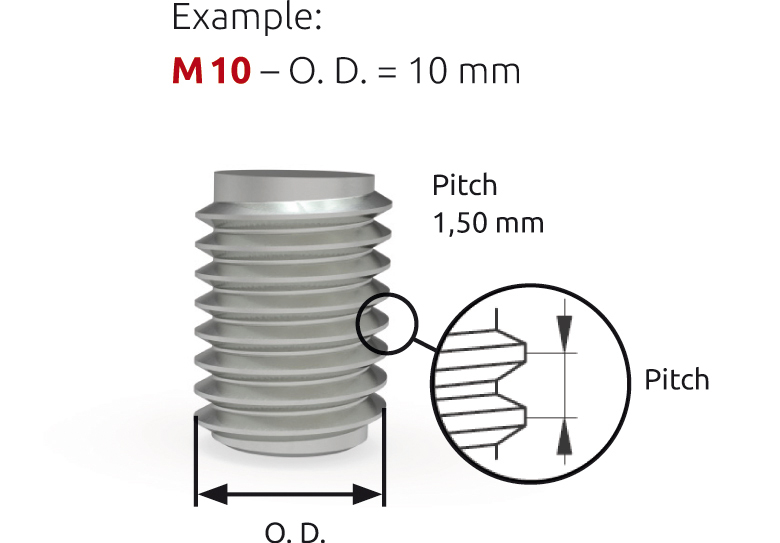
M (metric ISO thread)
- Cylindrical O. D. respectively I. D.
- Fine taper through metric thread
- best possible force transmission
- capital “M” plus an indication of nominal O. D., e. g. M 10
- deviating pitch from the standard is marked with an appendix, e. g. M 10 x 0,75.
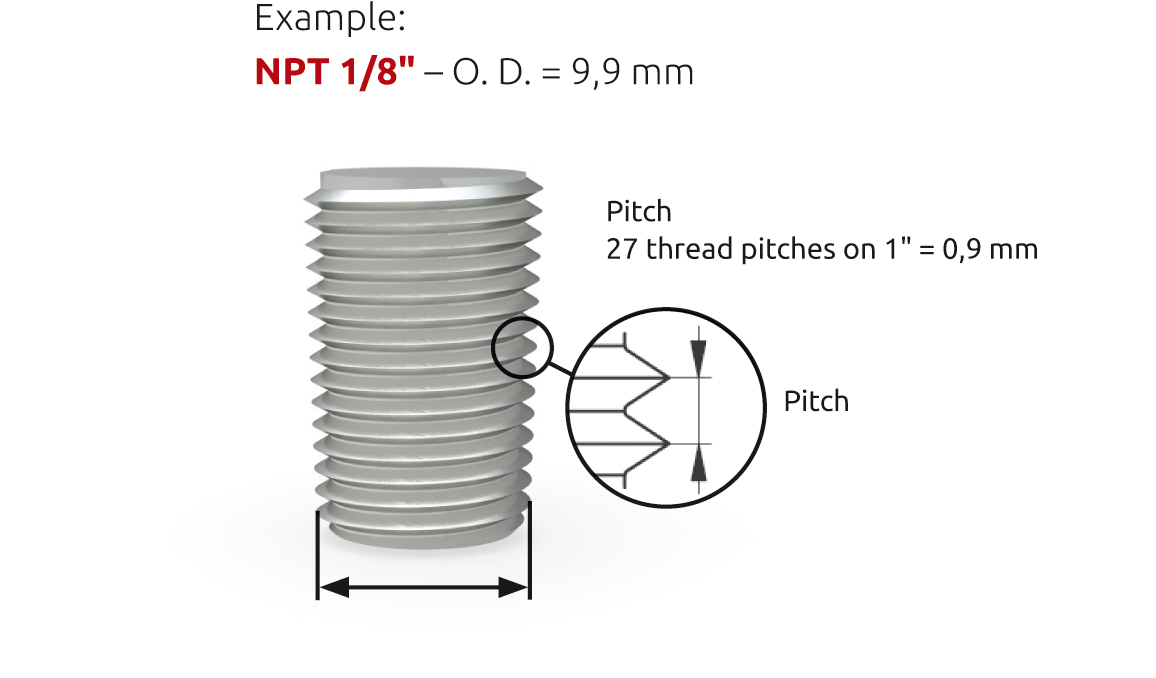
NPT
- tapered O. D. respectively I. D.
- self-sealing
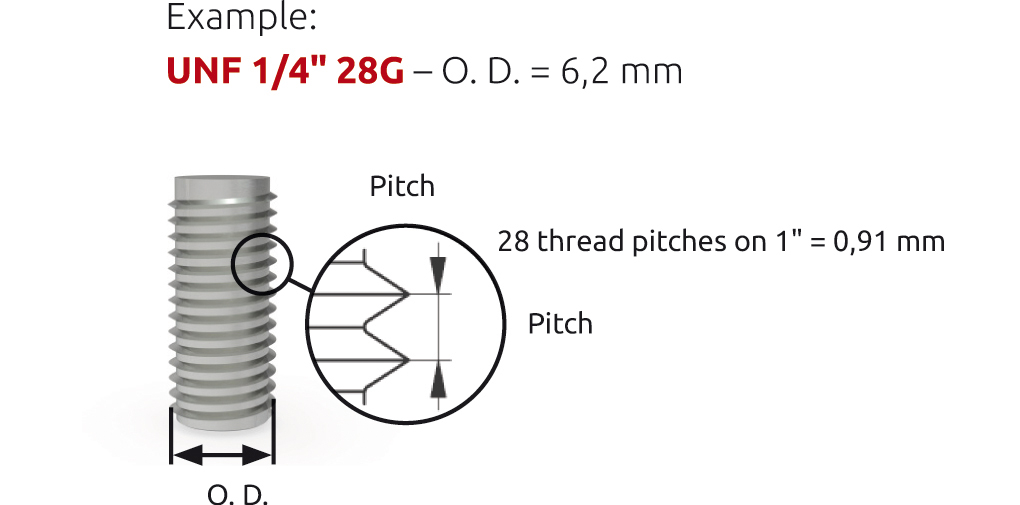
UNF 1/4" 28G
- Mainly used in chromatography / HPLC applications in the USA
- Digits 28 G and 32 G stand for the number of thread pitches at a length of one inch (25,4 mm)
UNF ¼” 28G versus M 6
b.safe Fittings come with the most common HPLC thread UNF ¼” 28 G without exception. In addition, fittings and distributors with the very similar thread M 6 exist. These threads can only be distinguished by exact determination of their outer diameter or by using a test mandrel (it is possible to screw in a tube end fitting in the counterpart of the other thread for at least 2-3 rotations). The UNF ¼” thread has an outer diameter of 6.35 mm, the M 6 thread has exactly 6 mm (work tolerances are possible). We recommend to use only the UNF ¼” 28G thread to avoid confusion and double inventory.
Measurement chart
Viewed


